Our Location
Islamabad, Pakistan

Welcome to our blog post in which we will discuss 50 amazing facts about the human body. The human body is a sophisticated, intricately designed system composed of distinct cells that cooperate to carry out the numerous tasks needed to maintain life. The most sophisticated and intellectual species on Earth is the human. One of nature’s cautions is, in reality, the human race. You have a really seductive constitution.
There are so numerous instigative and weird body facts about them that it’ll truly blow your mind. Intrigued? Want to know further about weird data about the human body? Well, if your answer is a big yes, also let’s unveil all the fun facts about the human body. Read ahead.
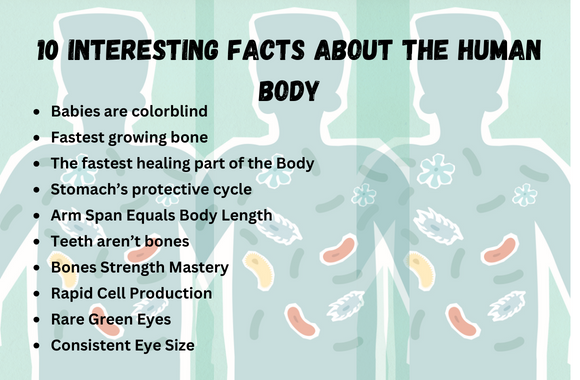
Following are 10 interesting facts about the human body, you weren’t familiar with earlier:
Let’s explain it one by one;
Babies cannot see color at birth. Throughout the first several months of life, their capacity to recognize color steadily grows.
The bone in the leg is the one that grows the fastest in the human body. Its development was characterized by its quick expansion.
The human tongue stands out as the swift-healing part of the body, representing amazing regenerative capabilities.
Every two weeks, the stomach must induce a new subcast of mucous filling to help tone- digestion, showcasing the pivotal part of this defensive medium, otherwise, the stomach will digest itself.
A person’s arm span, when completely stretched out, is equal to the length of their entire body, showcasing commensurable harmony.
Since teeth are an essential part of the skeleton, they are not included in bone counts. They are special to the function and wellness of the mouth.
In terms of strength per unit, bones are more robust than steel. A chunk of bone the size of a matchbox can withstand weights up to 18,000 pounds.
Your body produces 25 million new cells every second, which in only 15 seconds will outnumber the whole population of the United States. This incredible speed emphasizes how the human body’s cells are always active.
Green eyes are extremely rare; just 2% of people have them. All newborns have blue or brown eyes at birth, and between the ages of six months and three years, green eyes begin to appear.”
The size of your eyes remains relatively constant throughout your entire life.
These facts highlight the human body’s extraordinary talents and complicated nature. They highlight the remarkable qualities and intricate functions that make it a marvel of biological design. When taken as a whole, these facts demonstrate how astounding our physiological composition is. Sure, here are 10 fascinating and somewhat unbelievable facts about the human body:

Their explanation is;
Every individual possesses a one-of-a-kind point, lingo print, and indeed a unique scent. The combination of these related features is exclusive to each person, with the exception of identical halves, who may partake in identical sets of these characteristics.
Despite common belief associating strength with the heart, the title of the strongest muscle goes to the masseter the jaw muscle. Pound for pound, it has the capacity to ply further pressure than any other muscle in the human body.
The human body comprises trillions of cells. What adds to the seductiveness is that our bodies harbor roughly 10 times more bacterial cells than human cells. The microbiome, conforming to these bacteria, plays a vital part in maintaining our health.
The human body produces sufficient electricity to illuminate a small light bulb. This electrical miracle arises from the movement of ions in and out of cells, particularly within the nervous system.
Hair possesses remarkable strength, with a single beachfront able to support up to 100 grams in weight. On average, the crown houses roughly 100,000 to 150,000 hair follicles.
An existent blinks, on average, 15- 20 times per nanosecond, totaling around 28,800 blinks in a day. This rapid-fire eye movement serves the essential purpose of keeping the eyes moisturized and shielded from dust patches.
A sneeze can propel itself at a speed of over to 100 long hauls per hour. This underscores the significance of covering the mouth and nose during a sneeze to help the dispersion of origins.
If you were to extend all the blood vessels in your body end to end, they would gauge roughly 60,000 long hauls further than twice the Earth’s circumference.
The liver stands out as the sole organ capable of regeneration in the human body. Should a portion of the liver be removed, it can regenerate to its original size within many weeks.
The skin, the body’s largest organ, undergoes perpetual renewal. On average, an individual shanties about 600,000 skin patches every hour, equating to roughly 1.5 pounds of skin cells annually.

These psychological facts illustrate the amazing complexity of the human mind by illuminating subtleties in perception, memory, cognition, and social interaction. They provide an understanding of the many functions of the mind.

Mirror neurons in the brain are touched off not only when we engage in an action but also when we witness someone additional performing the same action, promoting empathy and appreciation.
Individualities who have experienced branch amputation may still feel sensations or pain in the missing branch, appertained to as phantom branch sensation, as a result of the brain’s patient representation of that body part.
Recollections of emotional gests are generally more robustly decoded, enhancing the liability of their retention in the memory.
The brain does not authentically multitask; rather, it fleetly shifts attention between tasks, performing with reduced effectiveness and the possibility of crimes.
Body language and facial expressions are examples of nonverbal cues that are extremely important in communication because they often convey information that spoken words cannot.
Neurotransmitters that are frequently associated with emotions of happiness and pleasure, such as dopamine, serotonin, oxytocin, and endorphins, are important for mood and well-being regulation.
When faced with opposing views or attitudes, people may experience cognitive dissonance, which is discomfort that prompts them to confront and correct the discrepancy.
Hormones like cortisol and adrenaline are released in response to stress, triggering the fight-or-flight response in the body.
The brain is very active during the rapid eye movement (REM) sleep phase when dreams are most common. The precise function of dreams is still not well understood.
The brain’s ability to sift through irrelevant information is known as selective attention, and it allows people to focus on certain stimuli while ignoring others.
People frequently exhibit superior memory for the first and last items on a list (primacy effect) and less vivid memory for the things in the middle (recency effect).
Occasionally, indeed in cases when a remedy has no real remedial benefit, the belief in its efficacy might lead to real physiological changes.
The circadian meter, which is the body’s internal timepiece, controls the sleep-wake cycle as well as a number of physiological functions, similar to body temperature and hormone conflation.
Hedonic adaption refers to the human capability to snappily return to a generally harmonious position of happiness, anyhow of important positive or negative life gests.
The brain’s capability to rearrange itself is known as neuroplasticity. It’s a point that helps the brain make new neural connections throughout life, acclimatize to new gests, and promote literacy.
Subconscious thinking patterns, feelings, and conduct are told by a significant quantum of internal exertion that occurs there without conscious knowledge.
The body can acclimate to its surroundings as its perceptivity to a static encouragement decreases. For illustration, as a result of this adaption, the smell of a room may gradationally fade.
The intricacy of the neural connections inside the brain affects intelligence instead of the size of the brain directly influencing intelligence.
People frequently have a propensity to look for, analyze, and retain information that confirms their preconceived notions, which leads to a skewed understanding of reality.
Emotions are infectious; we might unintentionally pick up on and change our mood from the presence of joyful or unhappy people.
The tendency for people to form preferences for items only because they are familiar with them is known as the simple exposure effect.

The human body is incredibly diverse; the regenerating liver and the complex gut bacteria are just two examples. Surprisingly, nutrition, cleanliness, and genetics all affect a person’s distinct aroma. Furthermore, the vast network of blood arteries would span almost 60,000 miles if put end to end. Five interesting facts concerning the human body are:

So here they are;
Blushing is a uniquely human reaction that causes the blood vessels in the skin to enlarge, giving the skin a crimson tint. Other animals do not exhibit this instinctive reaction, which is typically associated with feelings such as humiliation.
Every individual has a distinct smell that is impacted by genetics, food, and personal cleanliness, which allows others to recognize and remember them. Surprisingly, although having the same DNA, identical twins can smell differently.
Involuntary contractions of the diaphragm muscle and closure of the vocal cords cause hiccups, which can occasionally be felt by the mother but usually go away on their own. They can even occur in pregnancy.
The DNA found in each of the trillions of cells that make up the human body’s nuclei is around six feet long if unwound. All of the cells’ combined DNA could travel several times from Earth to the sun.
The normal person’s tongue contains around 10,000 taste buds, each of which has 50–100 taste receptor cells. Saliva production ranges from 0.5 to 1.5 liters per day, which is essential for breaking down food particles and detecting tastes.

The human body is a fascinating and sometimes quirky subject. Here are some amusing and interesting facts about the human body: The human body is a fascinating and sometimes strange subject. The following are some interesting and crazy fun facts about our body:

Following are its explanations;
We refer to the sensation of goosebumps as piloerection. Our animal ancestors instilled this reaction in us, which helps them seem bigger to fend off predators or trap more air to keep warm.
The human stomach is sometimes referred to as the “second brain” since it contains more neurons than the spinal cord roughly 500 million.
The release of adrenaline is responsible for the butterflies in the stomach that arise during tense or exciting occasions. This hormone causes the heart rate to increase and the body’s blood flow to be redirected.
Sweat has almost no smell. Sweating causes an unpleasant odor, which is caused by bacteria on the skin breaking down perspiration.
Researchers have found hundreds of different bacterial species in the belly button, a tiny and often overlooked area of the body that supports a diverse ecology of bacteria.

As the fabled center of human emotion, the heart is one of the most fascinating parts of our bodies. The heart is sometimes compared to James Brown’s organs since it beats about 100,000 times a day on average that’s 35 million beats a year.
According to Kraneveld, “the intestines are our most beautiful organs.” He draws attention to the intestinal neural system’s incredible intricacy by drawing comparisons to the human brain.
Serving as a unique picture of the neurological system, the retina displays a characteristic vascular pattern that is important for seeing early warning signs of diseases including diabetes, hypertension, and deteriorating brain health.
The intestines absorb every vitamin from meals.
Your skin is your body’s greatest organ.
Pain is not something the brain can feel.
An adult bladder can contain up to 400ml of fluids.
The heart beats over 115,000 times a day.
Due body’s complexity, flexibility, sensory systems, movement, brain power, immune system, reproduction, homeostasis, energy production, and resilience make it truly amazing.
The human body is a miracle, exhibiting remarkable pliability and exquisite intricacy due to the organs and systems working in perfect harmony. It is an extremely extraordinary creature because of its unparalleled resilience and design.
Our body’s structural structure is made up of bones, which support and shield our organs and systems.
With its amazing capabilities that demand appreciation, the human body is an awful illustration of natural manufacturing. Its inflexibility and intricate design are astounding. Indeed if certain statistics may feel funny, keep in mind that the human body is an inconceivable and intricate medium. Seeking information from dependable sources is essential if you want to enhance your understanding of how your body functions and your overall health.